Energy
Market Trends
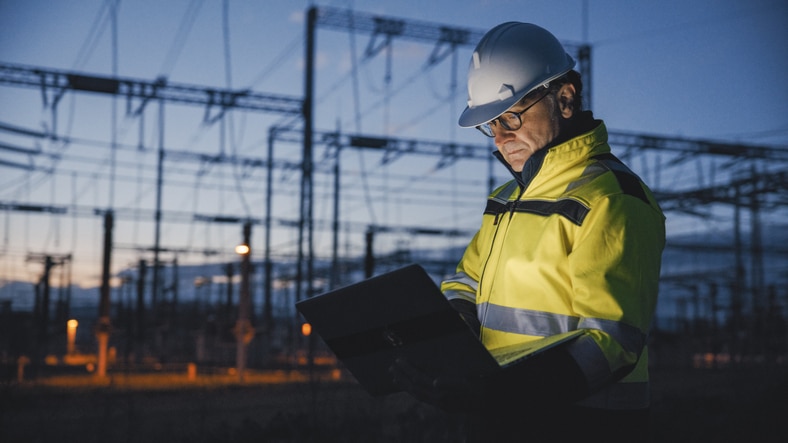
The oil, gas and energy sector is highly regulated and critical in keeping the country moving.
Workers face unique physical, mental, and environmental risks, making occupational health and safety a top priority.
Companies must implement comprehensive health programs, ergonomic interventions, mental health support, and regular health screenings.
Investing in employee well-being ensures compliance, enhances safety, and boosts operational efficiency.

Rise of Comprehensive Safety Management Systems: Advanced platforms are integrating safety assessments, absentee management and human-centric safety analytics to improve workplace health outcomes.
Health Data Integration and Wearable Technology: Wearable devices are tracking worker health metrics like fatigue, posture, and vital signs, allowing early interventions.
Health Risk Analytics and Predictive Modelling: Predictive analytics are being used to identify high-risk workers based on health data trends, allowing targeted safety interventions.
Digital Wellness Platforms and Mental Health Support: Companies are adopting digital wellness platforms that offer mental health resources, stress management tools, and well-being assessments to support worker wellness and productivity.
Automated Compliance Audits and Safety Checks: Digital audit tools are automating safety inspections and compliance checks, reducing human error and ensuring adherence to safety standards.
Challenges
Data Silos and Integration Issues: Health data is often stored in separate systems, making it difficult to consolidate and analyse for comprehensive safety insights.
Lack of Customisable Workflows: Rigid occupational health systems do not adapt to the unique needs of automotive manufacturing processes
Reactive Health Management: Occupational health processes are typically reactive rather than proactive, leading to delayed interventions and higher injury rates.
Poor Communication Across Teams: Ineffective communication between health, safety and HR departments delays response times and affects employee well-being.
Manual Compliance Tracking: Tracking compliance manually increases the risk of errors and makes it difficult to keep up with changing safety regulations.
Limited Employee Engagement: Employees often feel disconnected from occupational health processes, leading to underreporting of health concerns.
Complex Return-to-Work Processes: Coordinating return-to-work plans for injured employees is complicated without centralised health data and communication.
Underutilisation of Digital Health Tools: Despite the availability of digital health tools, many companies still rely on outdated systems, impacting efficiency and safety.
What Can Be Done?
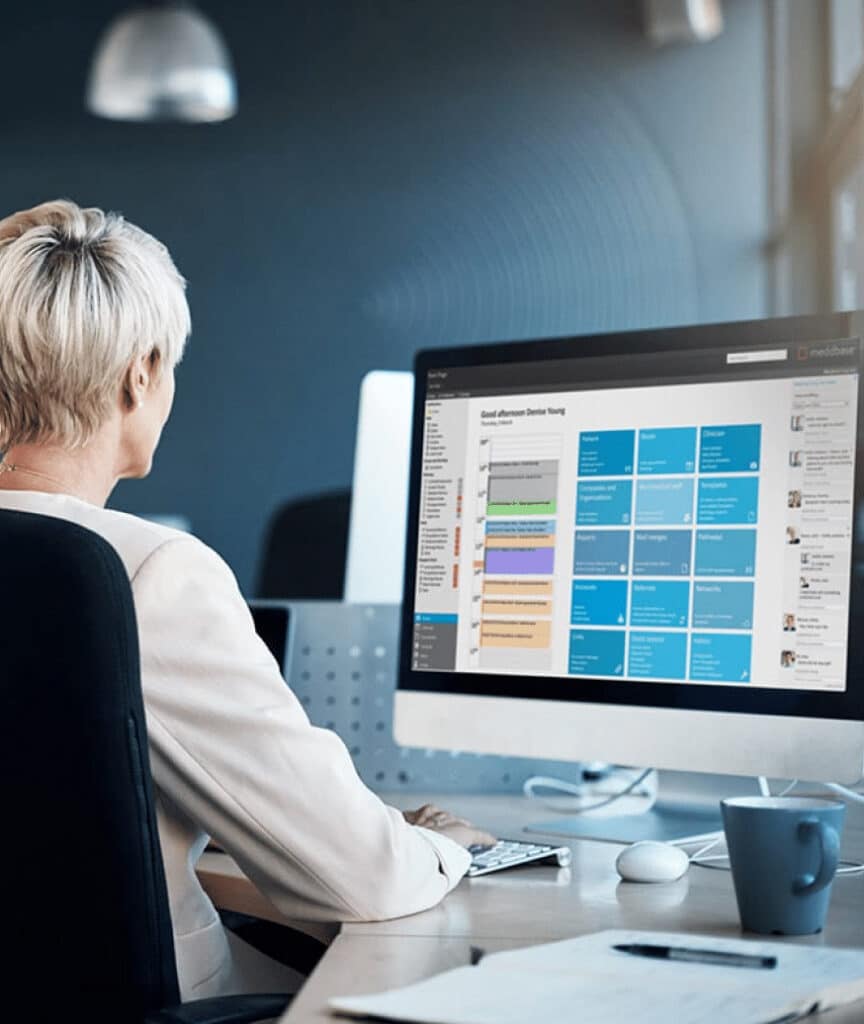
Automate workflows: EHR systems streamline scheduling, recordkeeping, and reporting, saving time and reducing errors.
Centralise data: Integrate occupational health data with HR and safety systems for holistic employee health insights.
Proactive risk management: Utilise data analytics to identify potential hazards, predict risks, and implement preventive measures.
Increase efficiency: Reduce paperwork, faster processes, and improved data accuracy.

Enhance compliance: Streamline reporting and audit trails demonstrate regulatory compliance.
Improve risk management: Proactive identification and mitigation of potential safety hazards.
Better employee health: Early detection and management of health conditions, leading to reduced work stoppages and improved well-being.
Cost savings: Increase operational efficiency, reduced compliance costs, and improved employee health outcomes.


