Aviation

Market Trends
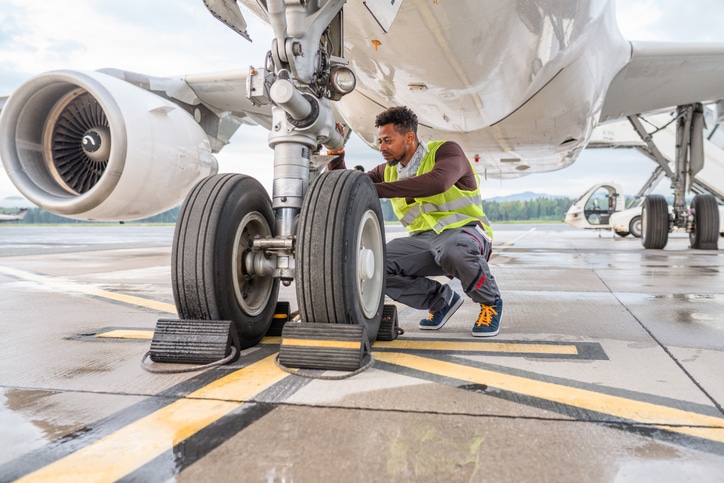
The aviation sector is highly regulated and critical to global transportation and logistics.
Workers face unique physical, mental, and environmental risks, making occupational health and safety a top priority.
Companies must implement comprehensive health programs, ergonomic interventions, mental health support, and regular health screenings.
Investing in employee well-being ensures compliance, enhances safety, and boosts operational efficiency.

Rise of Comprehensive Safety Management Systems: Advanced platforms are integrating safety assessments, absentee management and human-centric safety analytics to improve workplace health outcomes.
Data Silos: Disparate information across departments hampers timely and informed decision-making.
Visibility Issues: Difficulty in tracking health trends, identifying at-risk employees, and preventing incidents.
Non-Tailored Systems: Limited benefits and automation increase administrative burden and costs.
Fragmented Data Sources: Occupational health data scattered in spreadsheets, emails, and paper records prevent a holistic view of employee health.
Lack of Real-Time Insights: Delayed access to data impedes informed decision-making and proactive interventions.
Limited Reporting Capabilities: Manual reporting is time-consuming and error-prone, making it hard to demonstrate compliance and measure effectiveness.
Evolving Regulations: Keeping up with changing occupational health regulations is challenging.
Increased Penalties for Non-Compliance: Non-compliance with health regulations can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions.
Challenges
Manual Processes: Paper-based workflows lead to delays, errors, and non-compliance.
Lack of Customisable Workflows: Rigid occupational health systems do not adapt to the unique needs of automotive manufacturing processes
Reactive Health Management: Occupational health processes are typically reactive rather than proactive, leading to delayed interventions and higher injury rates.
Poor Communication Across Teams: Ineffective communication between health, safety and HR departments delays response times and affects employee well-being.
Manual Compliance Tracking: Tracking compliance manually increases the risk of errors and makes it difficult to keep up with changing safety regulations.
Limited Employee Engagement: Employees often feel disconnected from occupational health processes, leading to underreporting of health concerns.
Complex Return-to-Work Processes: Coordinating return-to-work plans for injured employees is complicated without centralised health data and communication.
Underutilisation of Digital Health Tools: Despite the availability of digital health tools, many companies still rely on outdated systems, impacting efficiency and safety.
What Can Be Done?
Automate workflows: EHR systems streamline scheduling, recordkeeping, and reporting, saving time and reducing errors.
Centralise data: Integrate occupational health data with HR and safety systems for holistic employee health insights.
Proactive risk management: Utilise data analytics to identify potential hazards, predict risks, and implement preventive measures.
Increase efficiency: Reduce paperwork, faster processes, and improved data accuracy.
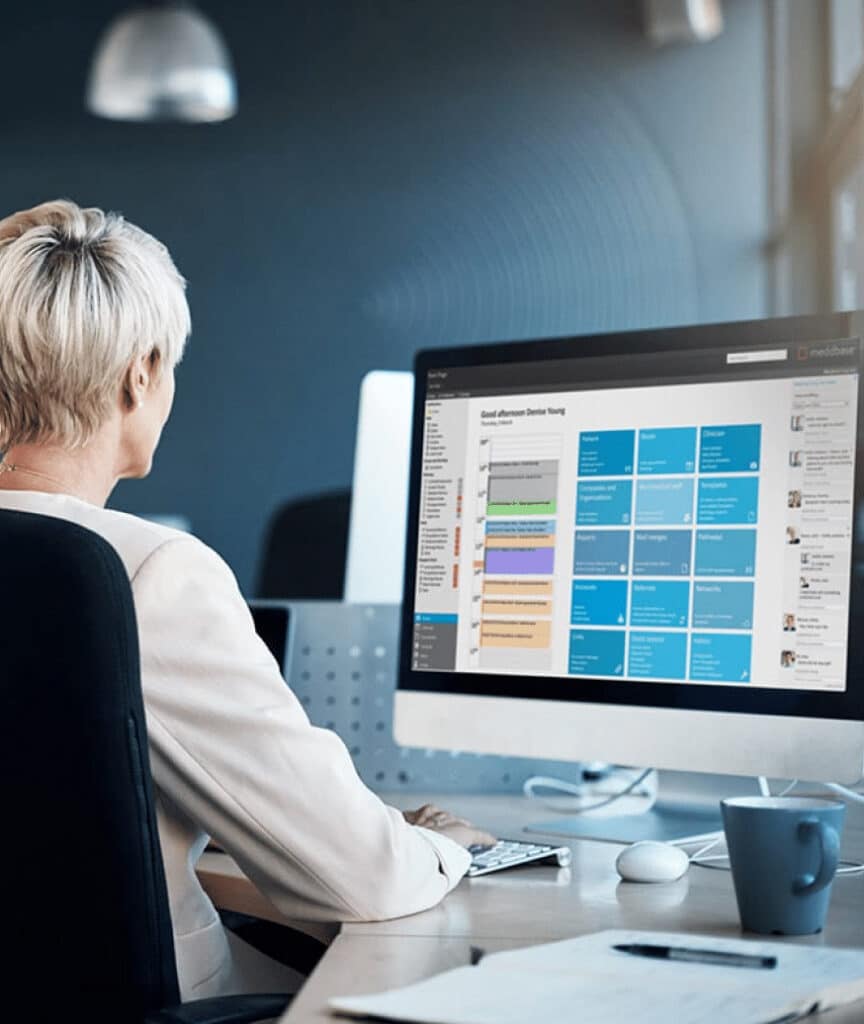

Enhance compliance: Streamline reporting and audit trails demonstrate regulatory compliance.
Improve risk management: Proactive identification and mitigation of potential safety hazards.
Better employee health: Early detection and management of health conditions, leading to reduced work stoppages and improved well-being.
Cost savings: Increase operational efficiency, reduced compliance costs, and improved employee health outcomes.

