Education

Market Trends
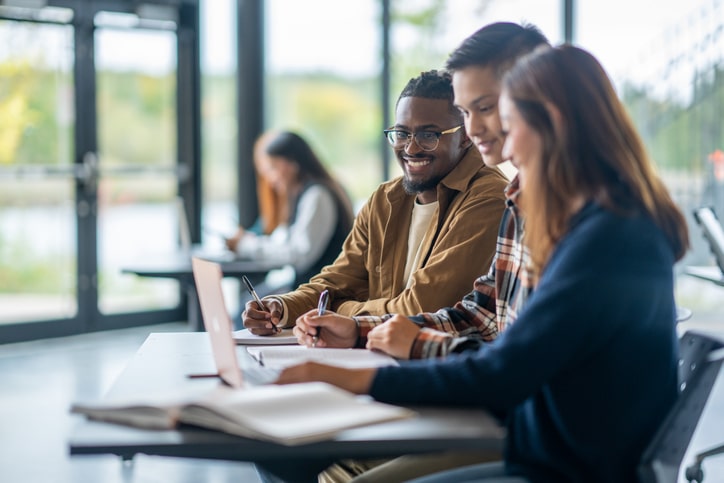
Universities are vibrant spaces that bring together people from diverse backgrounds; students, faculty, and staff, creating a dynamic and bustling environment.
However, managing occupational health and safety in such complex settings can be extremely challenging. With large populations spread across multiple departments and campuses, the risks are varied and widespread. Different departments face unique risks, from academic pressure to chemical hazards in research labs and safety concerns in public spaces.
Ensuring safety across a university requires coordinated efforts and comprehensive strategies tailored to its complex environment.

Holistic Mental Health and Wellness Approaches: Increased focus on comprehensive mental health programmes for students, staff, and faculty to combat stress, anxiety, and burnout.
Hybrid Learning and Working Environments: Blended on-campus and remote activities require flexible health and safety practices to support well-being.
Focus on Inclusivity and Accessibility: Growing demand for inclusive health solutions that cater to diverse needs, including students and staff with disabilities.
Increased Focus on Ergonomics and Physical Well-being: Universities are investing in ergonomic furniture and equipment to reduce musculoskeletal issues from prolonged sitting.
Health Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Rising use of health monitoring tools requires robust data privacy measures to protect sensitive health information.
Proactive Risk Management and Safety Training: Shift towards proactive risk management and continuous safety training to improve health literacy.
Community Health and Engagement Initiatives: Greater emphasis on community health programmes to create a culture of well-being and active participation.
Ergonomics Monitoring and Assessments: Ergonomics has become a key aspect of workplace safety, with universities investing in assessments and monitoring to prevent musculoskeletal issues.
Challenges
Scalability Issues: Occupational health systems often struggle to scale with growing student populations and expanding campuses.
Outdated Infrastructure and Legacy Systems: Old systems hinder integration with modern health tools, affecting data accuracy and accessibility.
Wide User Base and Complex Access Management: Universities serve a large population of students, faculty, and staff, making it challenging to manage health data access securely and efficiently.
Poor Flow of Information: Inconsistent communication channels lead to delayed health updates and important safety information not reaching all stakeholders effectively.
Inefficient Incident Reporting Systems: Complex and outdated reporting systems delay the identification and management of health and safety incidents.
Accessibility Challenges: Ensuring digital health tools are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is a persistent challenge.
Chemical and Lab Safety Risks: Exposure to hazardous chemicals and biological agents in labs poses safety risks.
Inconsistent Safety Policies: Variability in safety protocols across departments results in inconsistent health standards.
Workplace Violence and Security Threats: Public-facing roles, particularly in administration and security, face safety risks.
What Can Be Done?
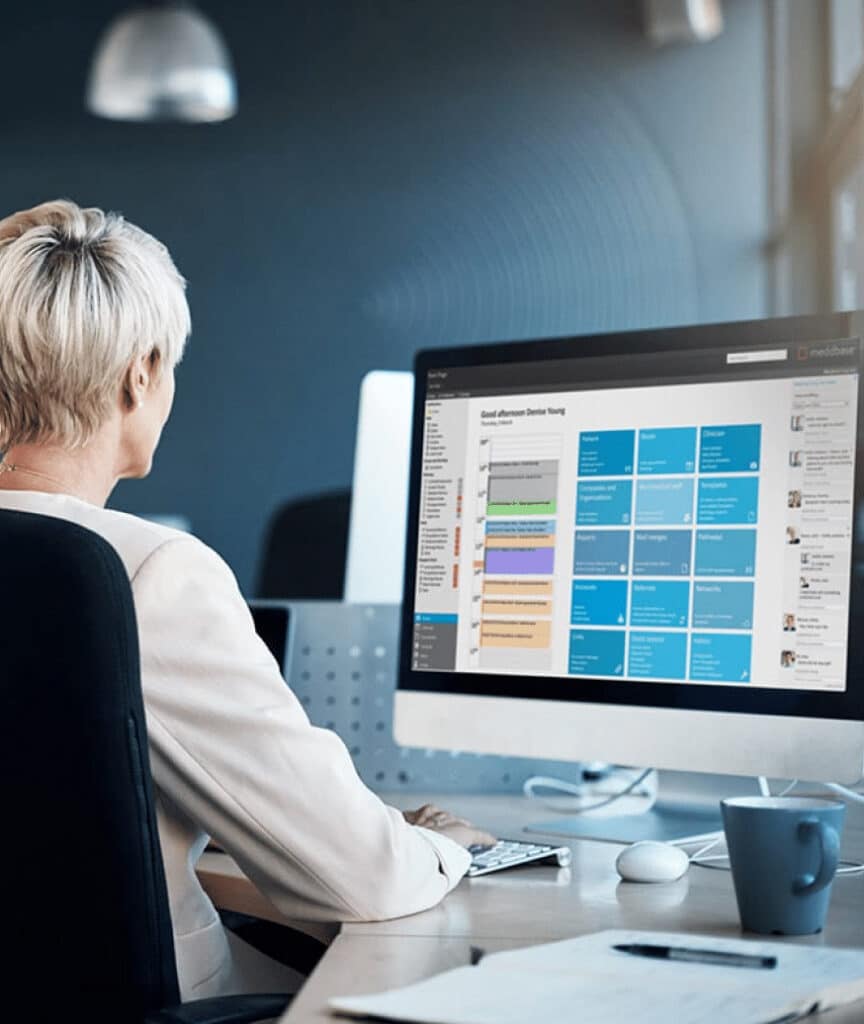
Automate workflows: EHR systems streamline scheduling, recordkeeping, and reporting, saving time and reducing errors.
Centralise data: Integrate occupational health data with HR and safety systems for holistic employee health insights.
Proactive risk management: Utilise data analytics to identify potential hazards, predict risks, and implement preventive measures.
Increase efficiency: Reduce paperwork, faster processes, and improved data accuracy.

Enhance compliance: Streamline reporting and audit trails demonstrate regulatory compliance.
Improve risk management: Proactive identification and mitigation of potential safety hazards.
Better employee health: Early detection and management of health conditions, leading to reduced work stoppages and improved well-being.
Cost savings: Increase operational efficiency, reduced compliance costs, and improved employee health outcomes.

